

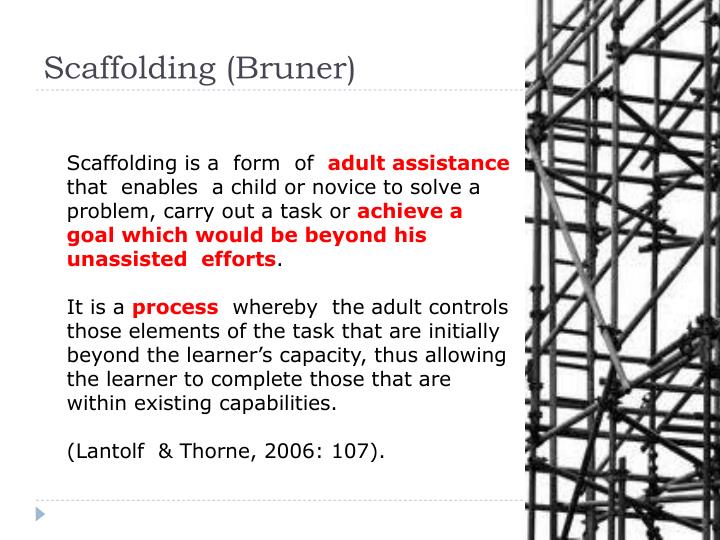
In an effective learning environment, scaffolding is gradually added, then modified, and finally removed according to the needs of the learner. Instructional scaffolding is most effective when it contributes to the learning environment. It is best to think of the use of instructional scaffolding in an effective learning environment as one would think of the importance of scaffolding in the support of the construction of a new building. The best and most effective use of instructional scaffolding helps the learner figure out the task at hand on their own. These concepts are learnt from more able peers or tutors, and thus Vygotsky needed to explain how these "higher psychological processes" are taught. This was based on the observation that a child could often recognise a solution before producing it, and the researchers hypothesised that it was here where teaching would be most beneficial.įor Vygotsky, the developmental process is more than about learning about basic concepts such as object permenance, but children need to acquire the "cultural tools" of a society, such as scientific or mathematical concepts, which can in turn effect behavior and cognition. Wood & Middleton's also termed the concept of the "recognition-production gap", although it defined slightly differently as the difference between what a child can recognise and what a child can produce. Critics have noted its similarity to the Vygotsky's ZPD and in later papers David Wood refers more to that. too much.ideally the child should be asked to add one extra operation or decision to those which he is presently performing". Confusingly, David Wood also has a term called the "region of sensitivity to instruction", which is circularly defined as the most effective level of instruction which "required the child to do more than he is immediately capable of. Vygtosky's zone of proximal development (ZPD) , describes the difference between what a learner can do alone and with the help of a more able individual, although he did not go into as much depth into the didactic process, which scaffolding describes. Zone of Proximal Development and related concepts 7.1 Efficacy of Instructional Scaffolding.

Demonstration or "modelling" of solutions of the task of a solution which has been partially solved by the learner.said that "problem solving should be less dangerous or stressful with a tutor than without". Fustration control of the learner, Wood et al.Marking critical features of a task and discrepencies between what the learner produces and what is correct.Keeping the learner's attention and motivation on the task and ultimite goal (each task may have several steps and goals which the learner gets stuck on), which is called direction maintaince.Other reseachers have called this contigent shifting.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
